What Is LAN & Wan Network?
What is Wi-Fi, LAN, and WAN?
In today’s digital age, we are surrounded by technology that keeps us connected to the world. Whether at home, in the office, or on the go, we use the internet to stay in touch, share information, and access a wealth of services. Three essential terms that play a vital role in this connectivity are Wi-Fi, LAN, and WAN. Understanding the differences between these technologies is important for anyone navigating modern networks, whether you’re setting up your home network or managing a corporate infrastructure.
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity)
Wi-Fi, short for Wireless Fidelity, is a technology that enables devices to connect to the internet or a network without the need for physical cables. It works by using radio waves to transmit data between a device, such as a smartphone, laptop, or tablet, and a wireless router. This router is usually connected to the internet via a wired connection and broadcasts a signal that allows nearby devices to connect wirelessly.
Wi-Fi has become a household name, especially because it provides mobility and convenience. You don’t need to plug in cables every time you want to access the internet, which is especially useful for mobile devices. Wi-Fi is widely used in homes, offices, cafes, airports, and public spaces, providing internet access to anyone within the router’s range.
There are different Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5, and Wi-Fi 6, with each offering improvements in speed, range, and capacity. Wi-Fi 6, for example, allows more devices to be connected at once while maintaining faster speeds and efficiency.
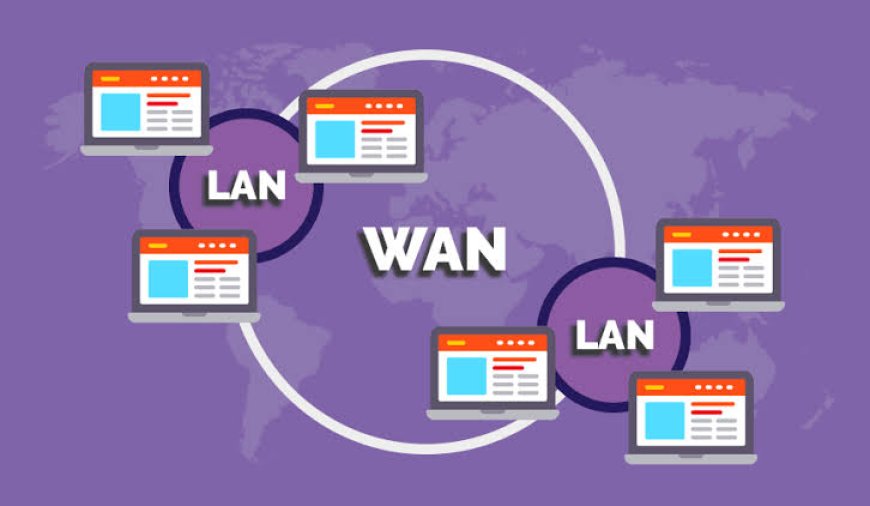
LAN (Local Area Network)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects devices within a limited geographic area, such as a home, office, school, or building. The primary purpose of a LAN is to allow devices like computers, printers, and storage devices to communicate with one another and share resources. This can include accessing the internet through a central router, sharing files, or printing documents on a shared printer.
LANs can be either wired or wireless. In a wired LAN, devices are connected through Ethernet cables, while in a wireless LAN, devices communicate via Wi-Fi. Typically, LANs are used in environments where a group of users need to share information or resources in close proximity. They are fast, reliable, and relatively easy to set up, which makes them popular in both residential and business settings.
In a home network, for example, your smartphone, laptop, and smart TV are all part of the same LAN, sharing internet access provided by the router. LANs can be scaled to suit different needs, from a few devices in a home to thousands of devices in a large corporation.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a much larger network that spans over a vast geographic area, often connecting multiple LANs together. WANs are used to connect devices across cities, countries, or even continents, and they can involve various communication technologies, such as leased lines, satellite links, or fiber optics.
The most well-known example of a WAN is the internet. The internet itself is a global WAN that links billions of devices worldwide, enabling seamless communication and data transfer across vast distances. Unlike LANs, which are confined to a single location, WANs connect multiple networks together to form a larger, more extensive communication system.
For businesses with offices in different locations, a WAN can connect each branch to the central network, allowing employees to access company resources and communicate with colleagues regardless of their physical location. In contrast to the relatively small and fast LAN, WANs tend to be slower due to the larger distances the data must travel and the more complex infrastructure required to maintain these networks.
### **Key Differences Between Wi-Fi, LAN, and WAN**
While these three technologies are interconnected, they serve distinct purposes. Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that allows devices to connect to the internet or a network without cables. LAN refers to a local network within a small area, like a home or office, that enables devices to communicate and share resources. WAN, on the other hand, connects multiple LANs across large distances, creating a network that spans cities, countries, and even continents.
Wi-Fi can be used within both LAN and WAN networks, providing wireless connectivity in environments where wired connections are not practical or possible. A LAN can exist with or without Wi-Fi, while a WAN typically requires high-speed, dedicated connections and infrastructure to function properly.
In conclusion, while Wi-Fi, LAN, and WAN are all integral to modern networking, they operate at different scales and are used for different purposes. Wi-Fi provides wireless access to networks, LANs enable communication within a local area, and WANs link multiple LANs over larger geographical distances. Understanding these technologies is key to optimizing and troubleshooting networks in both personal and professional settings.
What's Your Reaction?

















